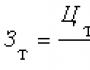Circulation circuit coolant. Engine cooling system circuit. Small and large engine cooling circle. We consider the coolant system does not circulate by a large circle
Mouse over the picture so that it becomes interactive.
Why do you need the engine cooling system can already be guessed from the name - working, the engine is heated and cooled through the radiator. It briefly. In fact, the task of the engine cooling system to maintain its temperature in a specific range (85-100 degrees), called the operating temperature. At operating temperature, the motor works as efficiently as possible and safely.
Large and small circle of engine cooling system
After starting, the engine should achieve the operating temperature as quickly as possible. For this, divided into two parts is a small circle and a large circle of circulation. At a small circle, the coolant circulates as close as possible to the cylinders and, accordingly, the most quickly heats up. As soon as it warms up to the highest working temperature, the valve opens and the liquid goes to a large circle where does not allow the engine to overheat. The task of a small circle to maintain the operating temperature, and large - to take off the excess heat.
Stove as part of the engine cooling system
It's nice when the interior is quickly warming up, and this happens because it is part of a small circle of circulation. Through the hoses, the liquid goes to the stove radiator and returns back. What does it mean? So that the stove began blowing warm air faster, it must be turned on when the engine is warm.

POMP and thermostat cooling system
So, we found out that the engine does not overheat due to the circulation of the coolant. But what makes the liquid move? The answer is. This is such a special pump, which is driven by the engine through the belt, but there are pumps and with an electric motor. Main faults Pumps associated with a flow through a drainage hole and bearing wear (accompanied by a pisk). There are also pumps with a plastic impeller, which is emerged from poor-quality antifreeze.
This most valve that opens when heating the coolant and keeps it in a large circle. Consists of a cylinder with a substance that expands when heated; Having achieved a certain temperature, it squeezes the rod and opens the valve. Colding, rod is drawn, and the valve closes.
Radiator and expansion tank engine cooling system
It is part of a large circle and is installed ahead of the car. It circulates the liquid, which is cooled by the oncoming air and the fan.
The fan works for suction, so as not to interfere with the counterflow of the air.
The radiator cover maintains pressure in the cooling system. It has a valve that opens when the pressure exceeds the working, and blends the extension fluid on the hose into the expansion tank.
Here how the engine cooling system is arranged. Among the main problems associated with this system are to allocate.
Strictly speaking, the term "liquid cooling" is not fully correct, since the fluid in the cooling system is only an intermediate coolant, penetrating the walls of the cylinder block wall. The role of the removal agent in the system plays air, blowing the radiator, so cooling the modern car is correct to name hybrid.
Device of the liquid cooling system
The liquid engine cooling system consists of several elements. The most complicated is called the "cooling shirt". This is an extensive network of channels in the thickness of the cylinder block and. In addition to the shirt in the system enters the radiator of the cooling system, the expansion tank, water pump, thermostat, metal and rubber connecting nozzles, sensors and control devices.
Propylene glycol - Base of coolant (antifreeze) and approved by veterinary doctors Food additive for dietary dogs
The system is constructed on the principle of forced circulation, which the water pump provides. Due to the constant outflow of the heated fluid, the engine is cooled uniformly. This explains the use of the system in the overwhelming majority of modern cars.
After passing through the channels in the walls of the block, the liquid heats up and falls into the radiator, where the air flow is cooled. When the car moves, it is quite natural enough to cool, and when the car is worthwhile, blowing occurs due to the electric fan, which turns on the signal from the temperature sensor.
Details about key elements of water cooling
Cooling radiator
The radiator is a panel of small-diameter metal tubes, covered to increase the heat transfer area by aluminum or copper "plumage". In essence, plumage, this is a multiple metal tape. The total total ribbon area is large enough, which means that there can be enough heat into the atmosphere per unit of time.
The most vulnerable element of the engine design is a turbocharger (turbine) operating at extremely high revs. When overheating, the destruction of the impeller and shaft bearings is almost inevitable
Thus, the warm-up liquid inside the radiator circulates immediately on all numerous thin tubes and is cooled quite intensively. In the lid of the radiator, the radiator is provided by a safety valve, a pair of and excess fluid expanding when heated.
Depending on the mode of operation, the FCs cycle of the coolant movement in the system may vary. The volume of fluid circulating in each circle directly depends on the extent to which the main and additional thermostat valves are open. This scheme provides automatic support for the optimal temperature mode of the engine.
Advantages and disadvantages of the liquid cooling system
The main advantage of the liquid cooling is that the engine cooling occurs evenly than in the case of blowing the air flow unit. This is explained by the greater heat capacity of the coolant compared to air.
The liquid cooling system allows to significantly reduce the noise from the working engine due to the greater the thickness of the block walls.
The system inertia does not allow the engine quickly after turning off. Preheat liquid of the car and for preheating combustible mixture.
Along with this, the liquid cooling system has a number of disadvantages.
The main disadvantage is the complexity of the system and that it works under pressure after heating the fluid. Pressure fluid places increased requirements for the tightness of all compounds. The situation is complicated by the fact that the operation of the system implies a constant repeat of the cycle "Heating - cooling". It is harmful for compounds and rubber pipes. When heated, the rubber is expanding, and then compressed when cooled, which becomes the causes.
In addition, the complexity and a large number of elements by itself serves as a potential cause of "technogenic disasters", accompanied by the "boiling" of the engine in case of failure of one of the key parts, for example, the thermostat.
Recall once again a little about this cooling system.
IN liquid cooling system Special cooling fluids are used - antifreeze of various grades having a thickening temperature - 40 ° C and below. Antifreeze contain anti-corrosion and anti-speaking additives, excluding scale formation. They are very poisonous and demand cautious. Compared to water, antifreeze has a smaller heat capacity and therefore remove heat from the walls of the engine cylinders is less intensively.
So, when cooling with antifreeze, the temperature of the walls of cylinders by 15 ... 20 ° C is higher than when cooling with water. It accelerates the engine heating and reduces the wear of the cylinders, but in the summer it can lead to engine overheating.
The optimal temperature mode of the engine with a liquid cooling system is considered to be such at which the temperature of the coolant in the engine is 80 ... 100 ° C on all modes of engine operation.
In car engines applied closed (hermetic) liquid cooling system with forced circulation Coolant.
The inner cavity of the cooling cooling system does not have a permanent connection with the environment, and the connection is carried out through special valves (at a certain pressure or vacuum), located in the radiator tubes or the expansion tank of the system. The coolant in such a system boils at 110 ... 120 ° C. Forced coolant circulation in the system is provided by a liquid pump.
Engine cooling system consists of:
- shirt cooling head and cylinder block;
- radiator;
- pump;
- thermostat;
- fan;
- expansion tank;
- connecting pipes and drain cranes.
In addition, the cooling system includes a car body salon.
Principle of operation of the cooling system
I propose to first consider the circuit circuit of the cooling system.
1 - heater; 2 - engine; 3 - thermostat; 4 - pump; 5 - radiator; 6 - plug; 7 - fan; 8 - expansion tank;
A - a small circle of circulation (the thermostat is closed);
A + b - a large circle circulation (the thermostat is open)
The circulation of fluid in the cooling system is carried out in two circles:
1. Small circle - The liquid circulates when the cold engine starts, providing its quick heating.
2. Big circle - The movement circulates when the engine is heated.
If it is easier to speak, then a small circle is circulation of coolant without a radiator, and a large circle - circulation of coolant through the radiator.
The cooling system device differ in its device depending on the car model, however, the principle of operation is one.
The principle of operation of this system can be seen in the following videos:
I propose to disassemble the system of the system on the sequence of work. So, the start of the cooling system occurs when the heart is started in this system - the liquid pump.
1. Liquid pump (Water Pump)
The liquid pump provides forced fluid circulation in the engine cooling system. On the engines of cars apply paddle pumps of centrifugal type.
Search our liquid pump or water pump should be on the front of the engine (the front part of this one, which is closer to the radiator and where the belt / chain is located).
The liquid pump is connected by the belt with the crankshaft and the generator. Therefore, to find our pump just find the crankshaft and find the generator. We will talk about the generator later, but so far only show what you need to look. The generator looks like a cylinder attached to the engine housing:
 1 - generator; 2 - liquid pump; 3 - crankshaft
1 - generator; 2 - liquid pump; 3 - crankshaft
So, the location was understood. Now let's look at its device. Recall that the device of the entire system and its details are different, but the principle of operation of this system is the same.
 1 - pump cover;2 - Stubborn sealing ring of the gland.
1 - pump cover;2 - Stubborn sealing ring of the gland.
3 gland; 4 - pump roller bearing.
5 - hub pulley fan;6 - locking screw.
7 - pump roller;8 - pump housing;9 - Pump impeller.
10 - receiving nozzle.
The pump work is as follows: the pump drive is carried out from the crankshaft through the belt. The belt twists the pump pulley, rotating the hub of the pump pulley (5). He in turn leads to rotation of the pump shaft (7), at the end of which the impeller is located (9). The coolant enters the pump housing (8) through the receiving nozzle (10), and the impeller moves it into the cooling shirt (through the window in the case, visible in the figure, the direction of movement from the pump is shown by the arrow).
Thus, the pump has a drive from the crankshaft, the liquid enters it through the receiving nozzle and goes into the cooling shirt.
Liquid pump work in this video (1:48):
Let's see now, how do liquid go to the pump? And the fluid comes through a very important part - the thermostat. It is the thermostat that is responsible for the temperature regime.
2. THERMOSTAT (THERMOSTAT)
The thermostat automatically adjusts the water temperature to accelerate the engine warming after starting. It is the work of the thermostat that determines how the coolant (large or small) will go.
This unit looks like this in reality:

The principle of operation of the thermostat Very simple: The thermostat has a sensitive element, inside of which the solid filler is located. At a certain temperature, it starts to melt and opens the main valve, and the optional on the contrary is closed.
Thermostat device:


1, 6, 11 - nozzles; 2, 8 - valves; 3, 7 - springs; 4 - cylinder; 5 - diaphragm; 9 - rod; 10 - filler
Thermostat work is simple, you can see it here:
The thermostat has two inlet nozzles 1 and 11, outlet nozzle 6, two valves (main 8, optional 2) and a sensitive element. The thermostat is installed before entering the coolant pump and connects to it through the nozzle 6.
Compound:
Throughpipe 1. Connect fromengine cooling shirt,
Through pipe 11. - With Lower disclosure Bulk radiator.
The sensitive element of the thermostat consists of a cylinder 4, rubber diaphragm of 5 and stock 9. Inside the cylinder between its wall and rubber diaphragm there is a solid filler 10 (fine-crystalline wax) with a high volume extension coefficient.
The main valve 8 of the thermostat with spring 7 begins to open at a coolant temperature of more than 80 ° C. At a temperature of less than 80 ° C, the main valve closes the yield of the fluid from the radiator, and it comes from the engine to the pump, passing through the opening additional valve 2 of the thermostat with spring 3.
As an increase in the temperature of the coolant more than 80 ° C in the sensitive element, a solid filler melts, and its volume increases. As a result, the rod 9 comes out of the cylinder 4, and the balloon moves up. An additional valve 2 begins to close and at a temperature of more than 94 ° C overlaps the coolant pass from the engine to the pump. The main valve 8 in this case opens completely, and the coolant circulates through the radiator.
The valve operation is clear and clearly shown in the figure below:

A - small circle, the primary valve is closed, bypass - closed. B - a large circle, the main valve is open, the bypass - closed.
1 - inlet nozzle (from the radiator); 2 - primary valve;
3 - thermostat housing; 4 - bypass valve.
5 - nozzle of the bypass hose.
6 - Cooling fluid supply pipe into the pump.
7 - thermostat cover; 8 - piston.
So, we dealt with a small circle. Disassembled the device and thermostat, connected. And now let's get to the big circle and the key element of the big circle - the radiator.
3. Radiator (Radiator / Cooler)
Radiator Provides the heat of the cooling fluid heat into the environment. On passenger cars apply tubular plate radiators.
So, there are 2 types of radiators: collapsible and not collapsible.
The bottom is presented to their description:

I want to say again about the expansion tank (Expansion Tank)

Next to the radiator or the fan is installed on it. Let's now turn to the device of this fan itself.
4. Fan (FAN)
The fan increases the speed and amount of air passing through the radiator. On the engines of cars, four- and hexadener fans are installed.
If a mechanical fan is used,
 The fan includes six or four blades (3), glued to the Cross (2). The latter is brought to the pulley of the liquid pump (1), which is driven by the crankshaft using the belt transmission (5).
The fan includes six or four blades (3), glued to the Cross (2). The latter is brought to the pulley of the liquid pump (1), which is driven by the crankshaft using the belt transmission (5).
As we previously talked, the generator (4) also enters the engagement.
If an electric fan is applied,

that fan consists of a 6 and fan motor 5. Fan - four-blade, attached to the motor shaft. The blades on the hub of the fan are located unevenly and at an angle to the plane of its rotation. This increases the flow of the fan and reduces the noise of its operation. For more efficient operation, the electric fan is placed in a casing 7, which is attached to the radiator. The electric fan is attached to the casing on three rubber bushings. The electric fan is turned on and off automatically sensor 3, depending on the coolant temperature.
So, let's summarize. Let's not alone and summarize on some picture. It is not necessary to emphasize on a specific device, but the principle of work should be understood, for it is the same in all systems, no matter how their device would not differ.

When starting the engine, the crankshaft begins to rotate. Through the belt transmission (I will remind you that it also contains the generator) is transmitted rotation to the pulley of the liquid pump (13). It leads to rotation shaft with an impeller inside the body of the liquid pump (16). The coolant enters the engine cooling shirt (7). Next, through the outlet (4), the coolant returns to the liquid pump through the thermostat (18). At this time, the thermostat is opened by a bypass valve, but closed the main one. Therefore, the fluid circulates through the engine shirt without the participation of the radiator (9). It provides quick engine warming. After the coolant is heated, the main thermostat valve opens and the bypass valve is closed. Now the fluid can not flow through the torus of the thermostat (3) and is forced to flow through the supply nozzle (5) into the radiator (9). There, the liquid is cooled and arrives back into the liquid pump (16) through the thermostat (18).
It is worth noting that some of the coolant comes from the engine cooling shirt into the heater through the nozzle 2 and returns from the heater through the nozzle 1. But we will talk about it in the next chapter.
I hope now the system will become understandable for you. After reading this article, I hope it will be possible to navigate in another cooling system, which realized the principle of operation of this.
I propose to read the same with the following article:
Since we affected the heating system, the next my article will be about this system.

In the separation of the human circulatory system into two circle of blood circulation, the heart is subject to less load than if the body had a common blood supply system. In a small circle of blood circulation, the blood goes to the lungs and then back through a closed arterial and venous system that connects the heart and lungs. Her path begins in the right ventricle and ends in the left atrium. In a small circle of blood circulation, blood with carbon dioxide carry arteries, and blood with oxygen - veins.
From the right atrium, the blood enters the right ventricle, and then through the pulmonary artery is injected into the lungs. From the right venous blood enters the artery and lungs, it gets rid of carbon dioxide, and then saturated with oxygen. According to the pulmonary veins, blood flows into atrium, then she enters a large circle of blood circulation and after that it is sent to all organs. Since in capillaries, she slowly, carbon dioxide has done to it, and oxygen - penetrate the cells. Since blood gets into the lungs under low pressure, the small circle of blood circulation is also called a low pressure system. The time of blood flow through a small circulation of blood circulation is 4-5 seconds.
With an increased need for oxygen, for example, at intensive sports, the pressure generated by heart increases, and the bloodstream is accelerated.
Big circle circulation
From the left ventricle of the heart begins a large circle of blood circulation. Oxygen-saturated blood gets out of the lungs in the left atrium, and then falls into the left ventricle. From there, arterial blood enters the artery and capillaries. Through the walls of the capillaries, blood is in the tissue fluid oxygen and nutrients, taking carbon dioxide and metabolic products. From the capillaries, it enters small veins forming larger veins. Then, according to two venous trunks (the upper hollow vein and the lower vein), it enters the right atrium, ending the big circle of blood circulation. A blood circuit in a large circulation circle is 23-27 seconds.
In the upper hollow vein, the blood flows from the upper parts of the body, and at the bottom - from the lower parts.
There are two pairs of valves in the heart. One of them is located between ventricles and atria. The second pair is located between ventricles and arteries. These valves provide the direction of blood flow and interfere with the reverse current of blood. The blood is injected into the lungs under greater pressure, and in the left atrium it falls under negative pressure. The human heart has an asymmetrical form: Since its left half performs more difficult, it is somewhat thicker than the right.
I propose to first consider the circuit circuit of the cooling system.
1 - heater; 2 - engine; 3 - thermostat; 4 - pump; 5 - radiator; 6 - plug; 7 - fan; 8 - expansion tank;
A - a small circle of circulation (the thermostat is closed);
A + b - a large circle circulation (the thermostat is open)
The circulation of fluid in the cooling system is carried out in two circles:
1. Small circle - The liquid circulates when the cold engine starts, providing its quick heating.
2. Big circle - The movement circulates when the engine is heated.
If it is easier to speak, then a small circle is circulation of coolant without a radiator, and a large circle - circulation of coolant through the radiator.
The cooling system device differ in its device depending on the car model, however, the principle of operation is one.
So, the start of the cooling system occurs when the heart is started in this system - the liquid pump.
Liquid pump (Water Pump)
The liquid pump provides forced fluid circulation in the engine cooling system. On the engines of cars apply paddle pumps of centrifugal type.
Search our liquid pump or water pump should be on the front of the engine (the front part of this one, which is closer to the radiator and where the belt / chain is located).
The liquid pump is connected by the belt with the crankshaft and the generator. Therefore, to find our pump just find the crankshaft and find the generator. We will talk about the generator later, but so far only show what you need to look. The generator looks like a cylinder attached to the engine housing:
 1 - generator; 2 - liquid pump; 3 - crankshaft
1 - generator; 2 - liquid pump; 3 - crankshaft
So, the location was understood. Now let's look at its device. Recall that the device of the entire system and its details are different, but the principle of operation of this system is the same.
 1 - pump cover; 2 - Stubborn sealing ring of the gland.
1 - pump cover; 2 - Stubborn sealing ring of the gland.
3 gland; 4 - pump roller bearing.
5 - hub pulley fan; 6 - locking screw.
7 - pump roller; 8 - pump housing; 9 - Pump impeller.
10 - receiving nozzle.
The pump work is as follows: the pump drive is carried out from the crankshaft through the belt. The belt twists the pump pulley, rotating the hub of the pump pulley (5). He in turn leads to rotation of the pump shaft (7), at the end of which the impeller is located (9). The coolant enters the pump housing (8) through the receiving nozzle (10), and the impeller moves it into the cooling shirt (through the window in the case, visible in the figure, the direction of movement from the pump is shown by the arrow).
Thus, the pump has a drive from the crankshaft, the liquid enters it through the receiving nozzle and goes into the cooling shirt.
Let's see now, how do liquid go to the pump? And the fluid comes through a very important part - the thermostat. It is the thermostat that is responsible for the temperature regime.
Thermostat (Thermostat)
The thermostat automatically adjusts the water temperature to accelerate the engine warming after starting. It is the work of the thermostat that determines how the coolant (large or small) will go.
This unit looks like this in reality:

The principle of operation of the thermostat Very simple: The thermostat has a sensitive element, inside of which the solid filler is located. At a certain temperature, it starts to melt and opens the main valve, and the optional on the contrary is closed.
Thermostat device:


1, 6, 11 - nozzles; 2, 8 - valves; 3, 7 - springs; 4 - cylinder; 5 - diaphragm; 9 - rod; 10 - filler
The thermostat has two inlet nozzles 1 and 11, outlet nozzle 6, two valves (main 8, optional 2) and a sensitive element. The thermostat is installed before entering the coolant pump and connects to it through the nozzle 6.
Compound:
Throughpipe 1. Connect fromengine cooling shirt,
Through pipe 11. - With Lower disclosure Bulk radiator.
The sensitive element of the thermostat consists of a cylinder 4, rubber diaphragm of 5 and stock 9. Inside the cylinder between its wall and rubber diaphragm there is a solid filler 10 (fine-crystalline wax) with a high volume extension coefficient.
The main valve 8 of the thermostat with spring 7 begins to open at a coolant temperature of more than 80 ° C. At a temperature of less than 80 ° C, the main valve closes the yield of the fluid from the radiator, and it comes from the engine to the pump, passing through the opening additional valve 2 of the thermostat with spring 3.
As an increase in the temperature of the coolant more than 80 ° C in the sensitive element, a solid filler melts, and its volume increases. As a result, the rod 9 comes out of the cylinder 4, and the balloon moves up. An additional valve 2 begins to close and at a temperature of more than 94 ° C overlaps the coolant pass from the engine to the pump. The main valve 8 in this case opens completely, and the coolant circulates through the radiator.
The valve operation is clear and clearly shown in the figure below:

A - small circle, the primary valve is closed, bypass - closed. B - a large circle, the main valve is open, the bypass - closed.
1 - inlet nozzle (from the radiator); 2 - primary valve;
3 - thermostat housing; 4 - bypass valve.
5 - nozzle of the bypass hose.
6 - Cooling fluid supply pipe into the pump.
7 - thermostat cover; 8 - piston.
So, we dealt with a small circle. Disassembled the device and thermostat, connected. And now let's get to the big circle and the key element of the big circle - the radiator.
Radiator (Radiator / Cooler)
Radiator Provides the heat of the cooling fluid heat into the environment. On passenger cars apply tubular plate radiators.
So, there are 2 types of radiators: collapsible and not collapsible.
The bottom is presented to their description:

I want to say again about the expansion tank (Expansion Tank)

Next to the radiator or the fan is installed on it. Let's now turn to the device of this fan itself.
Fan (FAN)
The fan increases the speed and amount of air passing through the radiator. On the engines of cars, four- and hexadener fans are installed.
If a mechanical fan is used,
 The fan includes six or four blades (3), glued to the Cross (2). The latter is brought to the pulley of the liquid pump (1), which is driven by the crankshaft using the belt transmission (5).
The fan includes six or four blades (3), glued to the Cross (2). The latter is brought to the pulley of the liquid pump (1), which is driven by the crankshaft using the belt transmission (5).
As we previously talked, the generator (4) also enters the engagement.
If an electric fan is applied,

that fan consists of a 6 and fan motor 5. Fan - four-blade, attached to the motor shaft. The blades on the hub of the fan are located unevenly and at an angle to the plane of its rotation. This increases the flow of the fan and reduces the noise of its operation. For more efficient operation, the electric fan is placed in a casing 7, which is attached to the radiator. The electric fan is attached to the casing on three rubber bushings. The electric fan is turned on and off automatically sensor 3, depending on the coolant temperature.
So, let's summarize.Let's not alone and summarize on some picture. It is not necessary to emphasize on a specific device, but the principle of work should be understood, for it is the same in all systems, no matter how their device would not differ.

When starting the engine, the crankshaft begins to rotate. Through the belt transmission (I will remind you that it also contains the generator) is transmitted rotation to the pulley of the liquid pump (13). It leads to rotation shaft with an impeller inside the body of the liquid pump (16). The coolant enters the engine cooling shirt (7). Next, through the outlet (4), the coolant returns to the liquid pump through the thermostat (18). At this time, the thermostat is opened by a bypass valve, but closed the main one. Therefore, the fluid circulates through the engine shirt without the participation of the radiator (9). It provides quick engine warming. After the coolant is heated, the main thermostat valve opens and the bypass valve is closed. Now the fluid can not flow through the torus of the thermostat (3) and is forced to flow through the supply nozzle (5) into the radiator (9). There, the liquid is cooled and arrives back into the liquid pump (16) through the thermostat (18).
It is worth noting that some of the coolant comes from the engine cooling shirt into the heater through the nozzle 2 and returns from the heater through the nozzle 1.