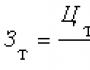Stimulation and motivation of personnel
Today we will talk about such a topic as: a tariff system of remuneration, and one of the discussions on Facebook came across this topic.
To begin with, we define that there is such a tariff system. Let us give this term for ease of writing, abbreviated species - TS.
TC includes the following:
- tariff standardization of labor;
- a tariff net for remuneration of workers in accordance with the complexity of the work performed (by the qualifications of employees) and, taking into account their personal business qualities;
- differentiation of tariff rates of the discharge on the significance of certain types of industries and works, their technological complexity, as well as the significance of the field of employment of labor;
- Supplements for work in working conditions deviating from normal, working conditions.
Now we will analyze every item in order.
Tariff regulation of labor Employees (the definition of the complexity of work and assignment of employee discharges) is based on the application of regulatory documents developed both in a centralized manner and directly within the company.
The centrally developed documents include:
- ETKS all issues;
- Qualification reference books of the RCC positions;
- OKPDTR.
The regulatory documents developed within the company include:
- a grouping of work on working conditions deviating from normal gravity, harmfulness, hazards for the health of workers, and other factors;
- Grouping of RCC posts on qualifying discharges of the tariff net. This may also include individual professions of workers not included in the ETKS or pro-sampled company;
- grouping of work on the categories of importance of the type of activity, the scope of employment and technological complexity to determine the differentiation coefficients of rates (salaries).
- full-time schedules (arrangements) by divisions that establish a qualifying and official division of labor between employees and ensuring the production functioning of the unit;
- Official (production) instructions of employees.
The goal is described separately, proceed by reference.
Tariff meshfor employee remuneration, workers have a uniform increase of rates from one qualifying discharge to another and provide for the range of initial monthly tariff rates (salaries) for each category designed to establish a tariff rate employee (salary). At the same time, monthly initial tariff rates are recalculated into hourly tariff rates by dividing them to the average monthly standards of working time, respectively, for 40-hour (36; 30) of the working week.
Hourly tariff rates for workers who have been installed 40-hour. Broadcast
| Interconnected step | COEF-T | Discharge | mIN. | med. | max |
| 1 | 1,00 | 1. | 64,00 ₽ | 67,00 ₽ | 106.00 ₽ |
| 1,13 | 1,13 | 2. | $ 72.50 | 75.50 ₽. | 120,00 ₽. |
| 1,13 | 1,28 | 3. | 82,00 ₽. | 85.50 ₽ | 135.50 ₽. |
| 1,13 | 1,45 | 4. | 92.50 ₽. | 96.50 ₽. | 153.00 ₽ |
| 1,13 | 1,63 | 5. | 104.50 ₽. | 109,00 ₽ | 173.00. |
| 1,13 | 1,84 | 6. | 118.00 ₽ | 123.00 ₽. | 195.50 ₽ |
| 1,13 | 2,09 | 7. | 133.50 ₽. | 139.00 ₽. | 221.00 ₽ |
| 1,13 | 2,36 | 8. | $ 151.00 | 157.00 ₽ | 249.50 ₽. |
Taking into account the differentiation, the tariff mesh may take the following form:
With information about the cost of one vehicle operating machine, the company has the opportunity to choose a supplier providing services for renting machines and mechanisms. We offer you a detailed algorithm for this calculation.
To determine the cost of the operation of the transport equipment, it is primarily necessary to calculate the cost of one machine-hour. This calculation is required in the following cases:
- the choice of transportation service provider for the needs of the enterprise. With information about the real cost of one machine-hour, you can choose the supplier on the most favorable terms. Market analysis in this case will not give objective information, since suppliers tend to obtain maximum profits;
- leasing for your own machines and mechanisms to third-party organizations. The correct calculation will allow to establish the optimal size of planned savings.
To determine the cost of one machine-hour of a certain type of vehicle, it is necessary to take into account the following indicators:
- balance cost of the vehicle;
- depreciation of the main means;
- the cost of performing all types of repair, diagnostic and maintenance;
- the cost of fuel and fuel and lubricants;
- payload of the driver taking into account deductions from wages;
- overheads.
Consider more each indicator and give examples of the calculation.
Balance cost of the vehicle- The cost of a vehicle reflected in the accounting documents, which, when purchasing a vehicle, is equal to the initial cost of the vehicle, and after the revaluation is equal to the restoration or complete reducing cost of the vehicle.
Amortization rate For each object of amortized property, when applying a linear method is determined by the formula:
- = (1 / n.) × 100%,
where K. - the rate of depreciation in percentages to the initial (restorative) value of the object of depreciable property;
N. - The term of useful use of this object of amortized property, expressed in months.
Note!
When establishing the timing of the useful use of fixed assets, it is necessary to be guided by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 01.01.2002 No. 1 "On the classification of fixed assets included in the depreciation groups" (as amended from 10.12.2010).
Regulatory the cost of performing all types of repair, diagnostic and technicalmachine maintenance is determined by the formula:
where in S. - restoration cost of the car, rub.;
N R - the rate of annual costs of repair and maintenance in percentage of the restoration cost of machines;
T. - Annual mode of operation of cars, Mash.-h / year.
Fuel costs and fuel and lubricantsit is possible to determine on the basis of the norms of fuel consumption and lubricants installed in a particular organization. Usually these norms are established and approved at the manufacturing meeting in the company.
It is also possible to be guided by the methodological recommendations of "FUILE COMPANY AND Lubricant Materials", approved by the order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia of March 14, 2008 No. AM-23-P (as amended by 05/14/2014).
Machinist's wages taking into account payroll deductionsdepends on the payment form in the company. The most common is a piecework and time-based form of remuneration.
Piecework Labor remuneration involves labor payment on the number of products manufactured (work) of established quality, taking into account complexity and working conditions. According to the adopted accounting procedure, the result of the work of each artist individually or collective (group) result (throughout the group of employees) can be taken into account.
With timeless formlabor is paid depending on the time spent on time, daily and monthly rates or salary. This form of payment is applied in cases where the development of a separate employee cannot be accurately accounted for and expressed in a certain amount of products or work or when it is economically inappropriate to translate workers to a piece of labor.
Example 1.
Initial data:
- the number of hours spent hours per month - 162;
- pricing for an hour set in the company - 130 rubles / h;
- the raising coefficient is 1.3.
Salary taking into account NDFL will be: 162 × 130 × 1,3 \u003d 27 378.00 rubles.
Payroll deductions: 27 378.00 × 0.3 \u003d 8213.4 rub.
____________________
Overheads accompany the main production associated with it. These are the costs of the maintenance and operation of fixed assets, management, organization, maintenance of production, for business trips, employee training and so-called unproductive costs (losses from downtime, damage material values, etc.). Overhead costs are included in the cost of production, the costs of its production and circulation.
Example 2.
Suppose in Example 1, industrial construction is considered. In accordance with the standards, overhead should be 90% of the wage foundation. Accordingly, the overhead costs will be: 27 378.00 × 0.9 \u003d 24,640,20 rubles.
______________________________
Consider an example of calculating the cost of 1 car hour.
Example 3.
Calculate the cost of 1 machine-hour operation of the car crane of the short-shaped zoomlion RT-550 with a loading capacity of 55 tons. To calculate the following data:
- balance Cost of the truck crane - 10, 3 million rubles;
- useful life - 61 month;
- the number of hours spent hours per month - 166;
- annual cost of maintenance costs and machine repair - 23%;
- tariff rate for wage - 140 rubles / h;
- fuel consumption rate for 1 mash / hour - 14, 3 l;
- cost 1 l foda - 27.34 rubles;
- the rate of consumption of lubricants per 100 liters of fuel consumption is 2 l;
- the cost of 1 l lubricants - 169,49 rubles;
- the rate of overhead costs is 90% of the foundation of labor payment.
The calculation is presented in the table.
|
Table 2. Calculation of cost 1 car operating machine |
||||
|
Name of the mechanism: A truck crane Short-shaped zoomlion RT-550, g / n 55 t |
||||
|
No. p / p |
Naming of expenditures |
unit of measurement |
Payment |
TOTAL |
|
Book value |
||||
|
Depreciation |
||||
|
Norm of monthly depreciation |
1/61 months. × 100% |
|||
|
Monthly amortization |
10 300 000.00 / 1.64% × 100% |
|||
|
Hour depreciation |
168 920,00 / 166,00 |
1 017,18 |
||
|
Maintenance costs and repair machines |
||||
|
Annual norm |
||||
|
Annual costs |
10 300 000.00 × 0.23 |
|||
|
Monthly costs |
2 369 000 / 12,00 |
|||
|
Hour expenses |
197 416,67 / 166,00 |
1 189,26 |
||
|
Labor Payment (Machine Salary) |
||||
|
Tariff rate, rub. / H |
||||
|
Insurance contributions |
||||
|
Hour salary |
||||
|
Fuel costs |
||||
|
Fuel consumption rate on 1 mash.-h |
||||
|
Cost 1 l fuels |
||||
|
Hour cost of fuel |
||||
|
Lubricant costs |
||||
|
Oil flow rate per 100 liter of fuel consumption (truck crane) |
||||
|
Oil consumption rate in accordance with the rate of consumption of fuction |
14.30 × 2.00 / 100 |
|||
|
Hourly costs for lubricants |
||||
|
Overheads |
||||
|
TOTAL Cost for 1 car hour |
1017,18 + 1189,26 + 182 + 390,96 + 48,47 + 126 |
|||
A. V. Makina, Economist LLC "Bomotk"
2.3 The calculation of the article "Costs per 1 km run" is made by the formula
where - the cost of fuel, den.ru / km;
Costs for lubricating and versatile materials, den.ied .. / km;
Costs for those. Service and maintenance, den.ru / km;
Costs for depreciation, den.ru / km;
Costs for repair and restoration of tires, den.ru / km;
Costs for salary drivers, den.ru / km;
Costs for overhead, den.ru / km.
2.4. Calculation of the article "Fuel Costs" is made by the formula:
![]() ,
,
where is the wholesale price of fuel;
Fuel consumption rate, l / 100 km;
The coefficient that takes into account the increased fuel consumption in the winter.
2.5 Calculation of the article "Costs for Lubricants and White Materials" is made by the formula:
where, - norms of consumption of machine, transmission oils and plastic lubrication per 100 km run.
Wholesale prices, respectively, oil used, den.ru
2.6 Calculation of the article "Maintenance costs and operational repair" is made by the formula:
where ![]() - Cost on costs of costs-1, TO-2, EO, den.;
- Cost on costs of costs-1, TO-2, EO, den.;
The average cost of current repairs per 1000 km of run;
![]() - regulatory mileage of the car to TO-1, TO-2, EO, km;
- regulatory mileage of the car to TO-1, TO-2, EO, km;
![]() ,
,
where is a coefficient that takes into account the reduction of operating costs for the new car.
2.7 Calculation of the article "Depreciation costs" is made by the formula:
![]() ,
,
where is the wholesale price, den .;
Annual car mileage, km;
Annual rate of depreciation deductions for the full restoration of the car,%,
Annual rate of depreciation deductions for the overhaul of the car,%.
2.8 Calculation of the article "Costs for restoration and repair of tires" is made by the formula:
![]() ,
,
where - Wholesale (retail) price for one bus, den.ed.;
Number of running tires, pcs.;
Shock absorption tire mileage, i.e. tires, km;
The coefficient, taking into account the cost of repairing tires.
2.9 The calculation of the article "The cost of salary of drivers" is made by the formula:
![]() ,
,
where is the tariff earnings of the driver, den.ru.;
Coefficient, taking into account surcharges and premiums;
12 - the number of months a year.
2.10. Calculation of the article "Costs for overhead" is made by the formula:
![]() ,
,
where is the standard of annual overhead costs for one car, den.ru
![]()
![]()
II. Drawing up estimation costs per 1 km run
Table 51. - Estimation of operating costs
| № | Expenditures | Amount, rubles | Result Appearance Saving |
|
| Base | New | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | Fuel costs | 0,0754 | 0,0742 | -0,0012 |
| 2 | Costs for lubricant | 0,00605 | 0,00608 | 0,00003 |
| 3 | Cost on | 1,035 | 1 | -0,035 |
| 4 | Depreciation costs | 0,0256 | 0,3023 | 0,2767 |
| 5 | Tire repair costs | 0,0075 | 0,0082 | 0,0007 |
| 6 | Salary costs | 0,0425 | 0,0386 | -0,0039 |
| 7 | Costs for overhead | 0,026 | 0,0236 | -0,0024 |
| 8 | TOTAL: | 1,21805 | 1,45298 | 0,23493 |
III. Costs per unit of transport work (cost1 T-km.) Are determined by the formula:
![]() ;
;
IV. Annual operating costs are calculated by the volume of transport work performed by the new car for the basic and new car:
![]() ,
,
where, - costs in operation for the year, respectively, according to the basic and new technique.
Part 3. Calculation of indicators of economic efficiency of new techniques.
I. The definition of conditionally annual economy (rise) is made in the three spheres:
3.1 in production:
![]() ,
,
where is the annual program for the release of new techniques.
3.2. In the field of operation:
![]() ,
,
3.3. In general, by national economy:
![]() ,
,
II. The definition of the annual economic effect on the national economy is made according to one of the above formulas:
3.4. If the new technique reduces costs, both in the field of production and in the field of operation, the economic effect is calculated by the formula:
3.5 If the new technique gives an economic effect only in the field of operation, and in production is more expensive, the economic effect is calculated by the formula:
3.6. If a new technique of increased quality (with a higher price), the economic effect is calculated by the formula.
Take the five most popular in our classes of cars - each in the most popular configuration - and estimate the cost of operation during the first three years, after which the factory guarantee usually ends and the car goes into other hands. Since many (not taxi drivers and no "snowdrops") each year rolling 20-25 thousand km, the total mileage for three years we accepted 70 thousand.
More precisely, the cost of spending the expenditure index. It shows how much a kilometer passed or one day of ownership of the machine. If you include in the calculation of washing, paid parking, unscheduled repairs, penalties for traffic violations, etc., indices will change significantly, but such spending depend on the mode of operation and the lifestyle of the owner, so we did not take into account them.
Entertaining arithmetic: the more expensive the car, the more money it will pull out during operationWhat do our calculations say? The conclusion is not new, although not everyone comes to himself. The more expensive the car, the more it will draw money in operation - because more expensive maintenance, consumables, insurance, and in a powerful machine with an automatic box and fuel consumption. Moreover, the expensive car is quickly depreciated with age - not in percentage, but in absolute terms: you will sell it much cheaper than bought new.
Of course, it is impossible to approach the purchase of a car purely rationally. We are moving not only the cold calculation, not to leave emotions. But a similar index clearly shows how expensive the car is burdensome for the family budget. Draw?