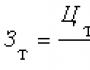What is the reimbursement of TSP funds. Facing commercial and service enterprises through a payment mediator (Serebryakov S.V.). PIN input requirement when paying a magnetic strip card
If a completely-quite simple language, this is a postal service.
Each participant of an IP-compatible network has its own address that looks like this: 162.123.058.209. Total addresses for the IPv4 protocol - 4.22 billion.
Suppose that one computer wants to contact the other and send him the parcel - "Package". He will contact the "postal service" TCP / IP and give her his parcel, specifying the address for which it must be delivered. Unlike the addresses in the real world, the same IP addresses are often assigned to different computers in turn, which means that the "postman" does not know where the necessary computer is physically located, so he sends the parcel to the nearest "post office" - on the network Computer board. Perhaps there is information about where the right computer is located, and perhaps there is no such information there. If it is not, the address of the address is taken to all the nearest "post offices" (switches). This step is repeated by all the "post offices" until they detect the desired address, while they remember how many "post offices" this request passed and if it passes a certain (sufficiently big) their quantity, then they will be returned back marked with the mark " Address not found. " The first "post office" will soon receive a bunch of answers from other "departments" with ways of paths to the addressee. If no short path is found (usually 64 shipments, but not more than 255), the parcel returns to the sender. If there is one or more paths, the parcel will be transferred along the shortest of them, while the "post office" will remember this path for some time, allowing you to quickly transmit subsequent parcels without asking anyone anyone. After delivery, "Postman" in obligatory Forced the recipient to sign the "receipt" that he received the parcel and give this "receipt" to the sender, as a certificate that the parcel was delivered to - check delivery to TCP is required. If the sender does not receive such a receipt after a certain period of time or in the receipt it will be written that the parcel was damaged or lost when sending, then he would try to send a parcel again.
Strike protocols, or in the Spatrical TCP / IP call network architecture modern devicesDeveloped to use the network. Stack is a wall in which each component of the brick lies on top of another depends on it. To call the TCP / IP Stack protocols began thanks to two main protocols that were implemented - directly IP and TCP on its basis. However, they are only the main and most suspended. If not hundreds, then dozens of others are used to this day for different purposes.
Our usual web (World Wide Web) is based on the HTTP Protocol (Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol), which is based on TCP based. This is a classic example of using the protocol stack. There are still IMAP / POP and SMTP email protocols, a remote SSH remote RDP desktop protocols, MYSQL, SSL / TLS databases, and thousands of other applications with their protocols (..)
What do all these protocols differ? Everything is quite simple. In addition to the various tasks set in developing (for example, speed, safety, stability and other criteria), the protocols are designed to distinguish. For example, there are application-level protocols, different applications: IRC, SKYPE, ICQ, Telegram and Jabber are incompatible with each other. They are designed to perform a specific task, and in this case the ability to call WhatsApp to ICQ is simply not defined technically, since applications use a different protocol. But their protocols are based on the same IP protocol.
The protocol can be called a scheduled, regular sequence of actions in a process in which there are several subjects, in the network they are called peers (partners), less often - client and server, emphasizing the specific protocol features. The simplest example of the protocol for not understanding still - a handshake at a meeting. Both know how and when, but the question is why it is already a matter of developers, and not users of the protocol. By the way, the handshake (Handshake) is almost on all protocols, for example, to ensure the distinction of protocols and protection against "flyers not on that aircraft."
That's what TCP / IP is on the example of the most popular protocols. Here is the dependence hierarchy. It must be said that applications only use these protocols that may be and may not be implemented inside the OS.
TCP / IP is a set of protocols.
The protocol is a rule. For example, when you greet you - you greet in response (and not forgive or unwaying happiness). Programmers will say that we use the welcome protocol, for example.
What the TCP / IP (now it will be quite simple, let the colleagues be bombed):
Information to your computer goes on the wires (radio or what else is not important). If the current let the current - it means 1. turned off - it means 0. It turns out 10101010110000 and so on. 8 zolkov and units (bits) is byte. For example 00001111. This can be represented as a number in binary form. In the decimal form byte is a number from 0 to 255. These numbers compare with letters. For example, 0 this A, 1 is B. (this is called encoding).
So. In order for two computers to effectively transfer information on wires - they must submit a current for some kind of rules - protocols. For example, they must be alleged how often the current can be changed so that 0 from the second 0 can be distinguished.
This is the first protocol.
Computers as it understand that one of them ceased to give information (like "I said everything"). To do this, at the beginning of the data sequence 010100101, computers can sly a few bits, the length of the message they want to transmit. For example, the first 8 bits can mean the length of the message. That is, first in the first 8 bits transmit the encoded number 100 and then 100 bytes. After that, the receiving computer will expect the following 8 bits and the following message.
Here we have another protocol, you can send messages (computer) with it.
Computers Many so that they can understand who needs to send a message to use unique addresses of computers and a protocol that allows you to understand who this message is addressed. For example, the first 8 bits will mean the recipient's address, the following 8 - the length of the message. And then the message. We have just stuck one protocol in another. The IP protocol is responsible for addressing.
Communication is not always reliable. For reliable delivery of messages (computer) use TCP. When executing the TCP protocol, computers will ask each other - whether they received the right message. There is still UDP - this is when the computers do not ask or they got. Why should I? Here you are listening to the Internet Radio. If a pair of byte comes with errors - you will hear, for example, "PSH" and then again music. Not mortally, and not much important - for this use UDP. But if a pair of byte is spoiled when the site is loaded - you will get a crap on the monitor and do not understand anything. For the site use TCP.
TCP / IP More (UDP / IP) is the protocols attached to each other on which the Internet is running. In the end, these protocols allow us to transfer a computer message to the whole and accurately at the address.
There is still an HTTP protocol. The first line - the address of the site, the subsequent lines - the text that you will go to the site. All http lines are text. Which is twisted in the TCP a message that is addressed by IP and so on.
ReplyNowadays, bank cards have ceased to be rare, and each of us has no one or two operations per quarter, but three or four daily. Tens of millions of released cards, hundreds of thousands of transactions per hour, tens of thousands of terminal devices for receiving cards - Such is today's reality. There is a steady tendency of the accent offset from the operations of receiving cash towards the payment of goods / services in trade and service enterprises (hereinafter - TSP).
Recall briefly, as generally looks like a payment procedure on a map in TSP.
The client (card holder) makes the purchase of goods or services in the TSP, which accepts cards to pay, as evidenced by stickers when entering the store room or at the checkout. Going to the cashier, the client places the card and informs the seller about what intends to pay with its help. The seller takes the map, holds her primary check on the lack of explicit signs of fake (he is not obliged to be an expert, just enough to make sure that it is clearly not fake). Next, the seller reads data from a magnetic strip or microprocessor (chip) of the card, using the corresponding electronic terminal connector for this (hereinafter - this). Then he introduces the amount of the operation, this generates an authorization request and sends to the bank-ear. Next, the authorization request on the MPS channel comes to the host of the issuer's bank, which allows or prohibiting this operation (transaction). If the transaction is permitted, the Issuer issues the authorization code and the response code (Response Code, Rc) '00'. Otherwise, the issuer's response is different from '00' and the authorization code is not issued (the transaction is not approved; The Issuer does not confirm the payment). With a positive conclusion, the TSP seller prints two copies of the check and the client confirms their consent to pay the transaction, or signing a check (Signature-based Transaction, SBT), or input PIN (PIN-Based Transaction, PBT). With SBT, the TSP seller must complete the operation by referring the signature on the check with a sample of the client signature in a specially designated place on the circulation of the card.
Placing information for buyers
Let's start with the fact that every TSP, sticking posters on its doors with MPS logos, thereby committing an obligation (it is the obligation, and not just a wish) to pay for the payment of the corresponding system.
Registration of payment transactions on bank cards in commercial and service enterprises
And if the cashier hangs the MasterCard logo, this TSP is obliged to accept the appropriate card (but not a Visa card, and vice versa). Moreover, in TSP, receiving maps, in places available to customers ("Corner of the Buyer"), information should be placed that explaining the policy of this point in terms of the return and exchange of goods paid on the map. The absence of such an information resource is a violation of the MPS rules.
Relocation of the cashier to accept the card
Quite often there are situations when, when entering the TSP, a sticker is hanging, saying that you can pay the card here, but at the time of payment suddenly it turns out that the cashier or the seller do not want to accept the card without explaining the reasons for refusal. Such actions are a serious violation of the Rules of the MPS and may entail the imposition of fairly tangible financial sanctions on a bank-acquirer, which in turn can broadcast them later on the trading point if it is provided for by the terms of the contract between them.
Passport requirement when paying a map
The rules of the MPS are completely definitely registered that when making payment on the map, the seller has no right to request from the client (map presenter) data confirming the identity of the latter, or other personal data, except when it is necessary to complete the transaction operation (for example, for Specifications of the address of the client's residence in order to follow the delivery of goods) or when it is clearly spelled out in the requirements of local legislation. The seller has no authority to demand a customer presentation of a passport or other identity documents. As a bright example, you can bring the following situation: Imagine that a customer from China or a citizen of a different exotic country is paid in the Russian TSP card, which does not own Russian or English. In this case, the seller and the buyer will not be able to communicate at all (of course, if the seller is not polyglot). From the point of view of the rules of the MPS, this practice of documents requirement when paying the card is punishable (a penalty of a bank-receipt can be imposed with all the consequences arising for TSP). However, some types of operations (to which, primarily include cash issuance operations in offices and branches of banks) should be committed only if the client has been presenting a document certifying the personality.
PIN input requirement when paying a magnetic strip card
Today, more and more banks produce cards equipped not only by a magnetic strip, but also a microprocessor (chip). Such cards are called hybrid, and you can perform operations for them - both by the magnetic strip and the chip. This is an undoubted advantage, as it is believed that the chip cannot be made at home, which, in turn, deprives the scammers of the possibility to make a fake card by releasing its duplicate with a copy of the magnetic strip track (so-called skimming). But often there is a situation where the seller of TSP, considering these card data from the magnetic strip (not from the chip), invites the client to confirm his consent with the commission of payment by introducing PIN. This is completely unacceptable, since the risk of full compromising the data of the card (i.e., the track / track of the magnetic strip and PIN), which theoretically could lead to the loss of all money from the card account. Sellers explain their actions by the fact that the electronic terminal is already programmed, but most often the error is lighted in their actions: when working with this, they indicate that the type of card is not MasterCard, but Cirrus / Maestro. It is noteworthy that in the territory of the Russian Federation all operations on Cirrus / Maestro cards must be committed precisely as PBT!
Interesting fact: in the rules of the VISA MPS, it is indicated that in any case, when performing the operation of payment for goods or services in the TSP, the client has the right to demand the SBT operation. And it has a completely reasonable explanation: not all customers remember their pin and some banks generally produce cards without pin to them. Of course, all of the above refers to the cards with a magnetic strip. By chip cards, the overwhelming number of operations in TSP is confirmed by the client by entering the PIN.
Recently, MasterCard MPS has released a circular (operating bulletin), in which he has notified all the participants in the calculations that from June 8, 2012 on the territory of the Russian Federation, I am allowed to request IDUs to confirm with clients of operations on maps with a magnetic strip conducted in TSP.
Thus, at present, in the territory of the Russian Federation, when placing operations in TSP on cards with a magnetic strip of the MPS Visa, the PIN input is invalid, and the MasterCard is allowed on the cards with a magnetic strip. By cards with a microprocessor (t. N. Chip), PIN is practically required for both MPS.
Refusal to accept cards without the name of the holder
Many issuers to quickly enter the market use so-called non-interstalized, non-mean cards, on the front side of which there is only a number, a validity period, but there is no surname and the name of the client (also these data, respectively, are absent on the first track of the magnetic strip). The rules of the IPU are completely clearly designated that such maps are an absolutely legitimate means of calculations and should be taken on par with all other MPS products. Equarers in the instructions for sellers also specifically stipulate this moment, and nevertheless, quite often, unfortunately, it happens that sellers flatly refuse to accept such cards to pay. As arguments, sellers bring an argument that they have nothing to compare the name and name of the client (meaning the prohibited practice of the request for confirming documents mentioned above). Such actions of TSP employees also contradict world practice and are subject to elaboration from the banks of the accreets.
Increase price (surcharge) for the goods when paying by the map
As you know, when concluding an accuming contract with TSP, the Bank indicates the size of the so-called parcel compassion (commission), which will be charged (underpaid) with TSP for all operations on the map. This Commission varies on countries and types of TSP activities, taking into account the revolutions of the latter. For a reference point, it can be borne in mind the amount of about 1.5 - 2.5%. Thus, if the amount of the transaction is 1000 rubles, the bank-accurate will credit the amount for the settlement of this commission, that is, 975 - 985 rubles. The difference is the most important component of the activities of the Equilera and will be attributed to the account of operating income. This is a completely normal practical practice worldwide, and the opinion that it is unprofitable for TSP is no more than delusion: when paying in cash, other overhead costs arise, quite comparable to these "losses" for acquiring. This includes the expenses of the TSP on passing cash, their safe storage, collection, etc. and nevertheless, many TPSs practiced the establishment of allowances when paying for goods and services on cards, and the size of such "cheats" is approximately equal to the size of the Exarcharge Commission. This practice is completely unacceptable, which is uniquely stipulated in the rules of the MPS. In the same rules of the MPS, a peculiar loophole for TSP is given, namely: it is indicated that TSP is entitled to provide a discount for cash. That is, in general, the price of goods or services when paying on the card should not exceed the usual, but you can make a discount to the client if it pays in cash.
Refusal to accept an unsigned card
According to the rules of the MPS on the reverse side of the map, a special band must be placed, intended for a sample of signature of the legal card holder. When executing the payment operation of goods or services in the TSP, the cashier must offer to the buyer to confirm its readiness to pay the deal, or by entering PIN, or by signing the electronic terminal check. If the consent is confirmed by the signature, the cashier should blame the signature on the check with a signature sample on the circulation of the card. However, quite often, when receiving a map, the client does not affect its signature (which is a violation of the requirements of the MPS and carries an increased risk of illegal use of the card by frauds in case of its loss). Sellers of the TSP, seeing that the client offers them an unsigned card, often refuse to accept such a payment facility to pay, which is also unacceptable. According to the rules of the MPS, in such cases, the cashier should offer to the Buyer to present a document certifying the identity of the latter, containing a photo and sample signature, after which it is suggested to sign a map, to merge the signature with the sample in the document and then complete the transaction. If the buyer fails to present a passport and (or) to sign the card, the transaction should not be completed.
Setting the minimum purchase / goods price to pay map
Often there are situations when the store comes out a minimum amount, starting with which the seller agrees to accept the card to pay. For example, the purchase amount when paying the card should not be less than 100 rubles. (or 1000, 10 000, etc.). This practice is categorically unacceptable, since according to the rules of the MPS, the terms of payment of the card must fully comply with the terms of payment of cash.
Return procedure for goods and tools spent
It happens that for any reason the client wishes to return the purchased goods back. If the goods were paid by the card, then the money must be returned to the card account, and not in cash. Moreover, the return of funds should be carried out at the expense of the card that the initial payment was made. If the goods return back, the Employee of the TSP should arrange an appropriate operation on the electronic terminal (Refund / Credit - Return / Credit). As a result of this operation, the terminal is printed a credit check, which is a confirmation and reason for the return of funds to the payer's account. According to the MPS rules, the return of funds must be carried out within 30 days from the date of registration of the loan operation. In the absence of cash receipt to the card account after this period, the client may issue a claim in the issuer, and the funds will be returned to the complaint cycle with the basis of "credit not solumed".
Registration of checks on card operations
The MPS imposes very strict requirements for the contents of the checks of electronic terminals, printed on the basis of the completion of the operation. So, the following data should be specified on the check:
- description / Price of each paid product / service;
- date and time of operation;
- the amount and currency of the operation;
- map number (for security reasons Only the last four digits);
- country, city, address of the point or separation of the bank;
- the name of the TSP or DBA (Doing Business AS, DBA Name, for example, VimpelCom OJSC is known in the market as Beeline);
- authorization code (if was);
- type of operation (payment of goods, refund);
- place to sign up the client;
- place for the initials of the seller, cashier or other identifier (for example, the department number in the supermarket) unit serving the card;
- place to sign a seller (in the case of a loan operation);
- on the copy of the buyer, the text in Russian or English should be placed approximately the following content: "Important: Save this check to control operations in the discharge";
- other parameters in accordance with the requirements of local laws.
According to the requirements of the Bank of Russia on the checks of Russian TSP, it is necessary to place the text about the amount of the commission (usually they are written "Commission of the Board is missing"), charged from the buyer.
It is also necessary to have the text of approximately the following content: "This is the authorization of its bank-issuer to pay this purchase and binding to compensate the issuer the amount marked in the column" Total ", plus all the relevant commissions."
Customers must store copies of checks for at least six months to ensure the ability to control the correctness of the write-off of funds in their statements on operations with the card. The main purpose of the information on the check is to ensure the ability to definitely relate information reflected in the discharge with the data on the check. If the data on the check and in the discharge differ significantly, the client arises the right to issue a claim with all the resulting sad consequences for the parlor.
Consideration of claims on the facts of identified violations
In all cases, the description of which is given in this article to affordable buyers - bank card holders need to be applying to only their bank-issuer who has released a card. In this case, it will be necessary to submit to the bank such data as the exact address of the TSP, the name, date, time, identifier or the name of the Bank of the Equilera (if the operation on the card did not take place at all, i.e. authorization request was not formed and did not go to the network , the Issuer will not be able to determine these data on its own), and the essence of the claim (refusal to accept the card, the requirement to present a passport, introduce a PIN, etc.).
Obviously, it makes no sense to even try to contact the accreede bank, since in general the situation with violation of the rules for registration of operations with cards may occur anywhere in the planet and not always the victim will be able to find time for a visit to the right place and it is unlikely that he will Enjoy special knowledge and own terminology at the local adverium.
Based on such an appeal, the issuer has full right to send, in turn, a claim to the authorized body of the IPU, and a variety of sanctions can be applied to the Equarer - ranging from warning and requirements to conduct additional training of employees of the TSP-violators, up to the imposition of tangible financial fines (hundreds and Thousands of dollars or euros depending on the tariffs of the MPS).
In our dynamic age, when non-cash payments rapidly invade all areas of life, and operations with bank cards became everyday phenomenon, the aspect of client literacy is very important. This question includes both the basics of the proper use of cards in everyday situations and the nuances covered in this article, namely: what rights to have a buyer when paying for goods or services in a network of trade and service enterprises on the map and what exactly needs to be taken in case Detection of violations of procedures for issuing such operations.
Since international payment systems do not work with end customers (cardholders and TSPs), and with financial institutions and primarily care that their products (maps) are accepted everywhere and without restrictions, the acquirers are made very strict requirements in terms of warranty and compliance with MPS card reception procedures in the network of their TSP. In cases of identifying violations of procedures and conditions for receiving cards, holders should complain about issuing banks, which in turn have the right and obligation to inform the corresponding MPS on such incidents, which ultimately may result in highly unpleasant sanctions for the boards and incorrectly working TRSs and their employees.
September 2012
Trade and service companies
The use of Cyberplat® Internet solutions (CyberPlat) has for trading companies A number of significant advantages, namely: the convenience and simplicity of the interface, the minimum document management, the rate of calculations and optimize the costs of receiving payments in trading and service points. The proposed technology for making calculations for receiving payments works exclusively in real time - the payer made funds to the cashier of the trade and service enterprise and instantly replenishes the settlement account of the service provider's company and the personal account of the payer in the billing system of the provider.
Ad
As a service provider, any organizations that provide services to the public (mobile operators, housing and communal services, electric generating companies, digital and cable television operators, Internet providers, satellite signaling systems and others are currently almost 4700 are currently.
To begin work, it is necessary to open the current account of the trade and service company in the KB "Platinum" and maintaining on the account of some working residue, within which the payment is made. At the time of the payment of the payment process, the client's personal account is replenished in ON-LINE mode, and cash funds are debited from the current account in the Platinum CB and are transferred to the operator's account.
A significant achievement of the Cyberplat® electronic payment system ("CyberPlat") is the ability to select a payment method and the use of various detection devices depending on the possibilities of dealers.
Payment can be carried out through the cashier:
- (for example, dealer company), using a computer connected to the Internet (or even a smartphone) and saving through the CyberPlat® website ("CyberPlat")
- using an automated cash register (for example, in the retail store) - in this case, interaction with the Cyberplat® electronic payment system ("cyberplat") is carried out through the server of the trading enterprise
- application of Technology "1C Enterprise"
- POS-terminals
- any phones and smartphones with Android support, iOS, Java
- other hardware.
and without human participation:
- payment Terminals (Cash-in)
- aTMs
For example,
- cash terminals are used for retail chains;
- for the Eldorado network - special technology using the internal network of the company;
- large dealer networks ("connected", "Euroset", "know-how", MTS retail network, Tele2 and others) apply a solution based on a web interface;
- small dealers and subdilers use "lightweight" versions of the client part of the software that can work including through GPRS.
The CyberPlat® system ("CyberPlat") leads to detailed accounting of all operations when using any of the following mechanisms, and full payments statistics are available in the on-line dealer administrator on the company's website
What is MCC code
MCC code — MERCHANT CATEGORY CODE. - Four-digit code reflecting the belonging of a trade and service enterprise to a specific type of activity.
A specific MCC code is assigned to the seller by the serving payment terminal by the Bank (Bank Equiler) at the time of installation of the terminal. If the trading point is engaged in several types of activity, then mCC code Assigns as code of the main activity (OKVED).
For different payment systems (Visa, MasterCard, peace, etc.), specific codes for one type of activity may differ, but in general they correspond to the following ranges:
- 0001 - 1499 - Agricultural sector;
- 1500 - 2999 - contract services;
- 3000 - 3299 - airline services;
- 3300 - 3499 - car rental;
- 3500 - 3999 - housing rental;
- 4000 - 4799 - Transport services;
- 4800 - 4999 - utilities, telecommunication services;
- 5000 - 5599 - Trade;
- 5600 - 5699 - Clothing stores;
- 5700 - 7299 - other stores;
- 7300 - 7999 - Business Services;
- 8000 - 8999 - Professional services and membership organizations;
- 9000 - 9999 - Public services
Why do you need a MCC code
Banks use MCC codes For the formation of statistics, analyzing the consumer behavior of customers, as well as for calculating cachek and bonuses According to loyalty programs.
What is this code for us to reasonable buyers? - for definitions of trading point to one category TSP And for the commission shopping with maximum benefitsusing a bank card with maximum cachekkom in the appropriate category.
How to find out the MCC code of a particular store
Before making a large purchase involving a large cache of one of your cards, it would be nice in advance to make sure that this purchase is accurately bonusing (rewarded) by the bank.
For this you need in advance (even before payment of the purchase) learn mcc code TSP. The following options are available:
1.
MCC code - what is what is needed, how to find out the category of TSP and where the cachek
MCC Codes Handbook
The easiest way is to contact mCC Codes Reference (eg, mcC-codes.ru.), and by searching by name and the city - find the point of interest and its MCC. It should be noted that there are mainly network and large stores in the directory, and possibly mCC code unpopular or local outlet Find will not work.
2. Map-flag storage and test (small) purchase
You can find out the MCC code by making a minor purchase with flameter maps (Maps in which the Internet Bank displays the MCC codes for operations). To such flag chemistry cards Believe:
3. Incomplete (not paid) Purchase with flag-flag
In order to learn mcc code this way, we need any card Bank Avangard. Define MCC-CODE The desired trading point can be as follows:
- Make sure in the zero balance of the card (or in the explicit lack of funds on the map on the test, "false purchase")
- Choose a "product of interest" in the store
- Make an unsuccessful attempt to pay for "purchase"
- After that, both in the Internet bank and in mobile application The unsuccessful payment operation will be reflected indicating MCC Code of the Trading Terminal.
After that you can choose the most profitable card for purchasing the MCC.
Do not forget to get acquainted with our list debit cards with cachekkom and percentage On the residue, it will help you choose the optimal version of the card. Also read: Top debit cards with cachemback on gas station.
1. General about resistance thermocouples.
Resistance thermocouples The number of the most common temperature converters used in measurement and regulation circuits are applied. Resistance thermocouples are produced by many domestic and foreign firms, such as Termico, Elemer (Moscow. Region), "Navigator", "Termautomatics" (Moscow), "Heat and Device" (Vladimir and Chelyabinsk) , Lutsk Instrument Plant (Ukraine), Siemens, Jumo, Honeywell, Foxboro, Rosemount (USA), Yokogawa (Japan), etc.
Thermometer of resistance A set for temperature measurement is called a thermal converter based on the dependence of electrical resistance from temperature, and the secondary instrument indicating the temperature value depending on the measured resistance. To measure the temperature, the resistance thermocouple must be immersed in a controlled medium and to measure its resistance to any instrument. According to a certain dependence between the resistance of the thermal converter and the temperature, the temperature value can be determined. Thus, the simplest set of resistance thermometer (Fig. 1, a) consists of a resistance thermocouple (TC), a secondary instrument (VP) for measuring the resistance and connecting line (LC) between them (it can be two, three or four-wire).
Fig. one. :
a - thermal converter with a secondary device; b - thermal converter with a normalizing transducer; TC - thermal converter of resistance; VP, VP1, VP2 - Secondary devices; LS - communication lines; NP is a normalizing converter; BRT - current reproduction unit
As a secondary device, analog or digital devices are commonly used (for example, KSM-2, RP-160, Tekhnographer, RMT-39/49), less often - logometers (for example, W-69001). Scale of secondary instruments are graded in degrees Celsius.
Schemes with the normalization of the output signal of thermal converters (Fig. 1, b) are widely used. In this case, the communication line the thermocoupleholder of the resistance is connected to the NP normalizing converter (for example, W-9321, IPM-0196, etc.) having a unified output signal (for example, 0 ... 5 or 4 ... 20 mA). To use in several measuring channels, this signal is propagated by the BRT reproduction unit and then enters several secondary instruments (VP-1, VP-2, etc.) or other consumers. Obviously, in this case, secondary devices should be milliammeters. Resistance converters are available, in which the rationing scheme is located, i.e. Their output signal is a current of 0 ... 5, 4 ... 20 mA or digital signal (intelligent transducers). In this case, the need to use the NP normalizing converter in the form of a separate block disappears. Resistance thermocouples with output unified signal They have in their designation the letter at (for example, TSPU, TSMU). The characteristics of these converters and with a digital output signal (metran-286) are given in Table. one.
Table 1
Technical data of resistance thermocouples
Type of resistance thermocouple | Admission class | Use interval, ° С | Limits of permissible deviations ± δ t, ° С |
0.15+ 0,0015 * | T | 0.25 + 0.0035 * | T | 0.50 + 0.0065 * T | |
|||
100 ... 300 and 850 ... 1100 | 0.15 + 0.002 * | T | 0.30 + 0.005 * | T | 0.60 + 0.008 * | T | |
||
TSPU | 0.25; 0.5% (cited) |
||
TSMU | 0.25; 0.5% (cited) |
||
KTP | 0 ... 180 Δ T. | 0,05 + 0,001Δ T.0.10 + 0.002δ. t. |
|
Metran 286. Output 4 ... 20 mA HART protocol | 0 ... 500 (from 100p) | 0.25 (digital signal) 0.3 (current signal) |
For the manufacture of thermal converters of resistance (TC), either pure metals or semiconductor materials can be used. The electrical resistance of pure metals increases with increasing temperature (their temperature coefficient reaches 0.0065 K-1, i.e. The resistance increases by 0.65% by increasing the temperature per degree). Semiconductor resistance thermocouples have a negative temperature coefficient (i.e., their resistance decreases with increasing temperature), giving up to 0.15 K-1. Semiconductor TCs are not used in technological control systems to measure temperature, as they require periodic individual graduation. Usually they are used as temperature indicators in the schemes for compensating the temperature error of some measurement tools (for example, in the circuits of conductometers).
Thermal converters resistance from pure metalswho were most common, usually manufactured from thin wire in the form of winding on a frame or spiral inside the frame. This product is called a sensitive element of the resistance thermocouple. For damage protection, the sensitive element is placed in protective reinforcement. The advantage of metallic TC is the high accuracy of temperature measurement (with low temperatures higher than that of thermoelectric transducers), as well as interchangeability. Metals for sensitive elements (CE) must meet a number of requirements, the main of which are the requirements of the stability of the graduation characteristics and reproducibility (that is, the possibilities of mass production of the CE with the same in the limits of the permeability of the error with gradual characteristics). If at least one of these requirements is not performed, the material cannot be used to make the thermocouple resistance. It is also desirable to perform additional conditions: a high temperature coefficient of electrical resistance (which provides high sensitivity - the increment of resistance to one degree), the linearity of the calibration characteristic R (t) \u003d f (t), a large resistivity, chemical inertness.
According to GOST R50353-92, resistance thermocouples can be made from platinum (designation TSP), copper (designation TSM.) or nickel (designation TSN). The TC characteristic is their resistance R0 at 0 ° C, the temperature coefficient of resistance (TKS) and class.
The presence of impurities in metals reduces the temperature coefficient of electrical resistance, so metals for the thermal converter of resistance must have normalized purity. Since TKS can change with a temperature change, the value of the purity is the value of W100 - the ratio of the TC resistance at 100 and 0 ° C. For TSP W100 \u003d 1.385 or 1,391, for TSM W100 \u003d 1.426 or 1,428. The class of the resistance thermocouple determines the permissible deviations and from the nominal values, which, in turn, determines the allowable absolute error of the Δt conversion of the vehicle. According to the permissible errors, the TS are divided into three classes - A, B, C, while the platinum TS is usually produced by classes A, B, copper - classes B, C. There are several standard vehicles. The nominal static characteristic (NCX) of the thermal processor of the resistance is the dependence of its resistance R, on temperature T
Symbol their nominal static characteristics (NCX) consists of two elements - the numbers corresponding to the value R0 and the letter that is the first letter of the material name ( P - Platinum, M - Copper, N - Nickel). In international designation, the Latin designations of materials Pt, Cu, Ni are located before the value of R0. NCM resistance thermal converters is recorded in the form:
where Rt is the resistance of the TC at a temperature T, Ohms; WT is the value of the resistance ratio at a temperature T to the resistance at 0 ° C (R0). WT values \u200b\u200bare selected from GOST R50353-92 tables. The ranges of the thermocoupleholders of the resistance of various types and classes, the formula for calculating the limit errors and Nsx are given in Table. 1 and 2.
table 2
Nominal static characteristics of resistance thermocouplers
| t ° C. | |||||||||
Nowadays, it has ceased to be rare, and each of us has no one or two operations per quarter, but three or four daily. Tens of millions of released cards, hundreds of thousands of transactions per hour, tens of thousands of terminal devices for receiving cards - Such is today's reality. There is a steady tendency to displace the accent from towards the operations of payment of goods / services in trade and service enterprises (hereinafter - TSP).
Recall briefly, as generally looks like a payment procedure on a map in TSP.
The client (card holder) makes the purchase of goods or services in the TSP, which accepts cards to pay, as evidenced by stickers when entering the store room or at the checkout. Going to the cashier, the client places the card and informs the seller about what intends to pay with its help. The seller takes the map, holds her primary check on the lack of explicit signs of fake (he is not obliged to be an expert, just enough to make sure that it is clearly not fake). Next, the seller reads data from a magnetic strip or microprocessor (chip) of the card, using the corresponding electronic terminal connector for this (hereinafter - this). Then he introduces the amount of the operation, this generates an authorization request and sends to the bank-ear. Next, the authorization request on the MPS channel comes to the host of the issuer's bank, which allows or prohibiting this operation (transaction). If the transaction is permitted, the Issuer issues the authorization code and response code (Response Code, RC) "00". Otherwise, the issuer's answer is different from "00" and the authorization code is not issued (the transaction is not approved; the issuer does not confirm the payment). With a positive conclusion, the TSP seller prints two copies of the check and the client confirms their consent to pay the transaction, or signing a check (Signature-based Transaction, SBT), or input PIN (PIN-Based Transaction, PBT). With SBT, the TSP seller must complete the operation by referring the signature on the check with a sample of the client signature in a specially designated place on the circulation of the card.
Placing information for buyers
Let's start with the fact that every TSP, sticking posters on its doors with MPS logos, thereby committing an obligation (it is the obligation, and not just a wish) to pay for the payment of the corresponding system. And if the cashier hangs the MasterCard logo, this TSP is obliged to accept the appropriate card (but not a Visa card, and vice versa). Moreover, in TSP, receiving maps, in places available to customers ("Corner of the Buyer"), information should be placed that explaining the policy of this point in terms of the return and exchange of goods paid on the map. The absence of such an information resource is a violation of the MPS rules.
Relocation of the cashier to accept the card
Quite often there are situations when, when entering the TSP, a sticker is hanging, saying that you can pay the card here, but at the time of payment suddenly it turns out that the cashier or the seller do not want to accept the card without explaining the reasons for refusal. Such actions are a serious violation of the Rules of the MPS and may entail the imposition of fairly tangible financial sanctions on a bank-acquirer, which in turn can broadcast them later on the trading point if it is provided for by the terms of the contract between them.
Passport requirement when paying a map
The rules of the MPS are completely definitely registered that when making payment on the map, the seller has no right to request from the client (map presenter) data confirming the identity of the latter, or other personal data, except when it is necessary to complete the transaction operation (for example, for Specifications of the address of the client's residence in order to follow the delivery of goods) or when it is clearly spelled out in the requirements of local legislation. The seller has no authority to demand a customer presentation of a passport or other identity documents. As a bright example, you can bring the following situation: Imagine that a customer from China or a citizen of a different exotic country is paid in the Russian TSP card, which does not own Russian or English. In this case, the seller and the buyer will not be able to communicate at all (of course, if the seller is not polyglot). From the point of view of the rules of the MPS, this practice of documents requirement when paying the card is punishable (a penalty of a bank-receipt can be imposed with all the consequences arising for TSP). However, some types of operations (to which, primarily include cash issuance operations in offices and branches of banks) should be committed only if the client has been presenting a document certifying the personality.
PIN input requirement when paying a magnetic strip card
Today, more and more banks produce cards equipped not only by a magnetic strip, but also a microprocessor (chip). Such cards are called hybrid, and you can perform operations for them - both by the magnetic strip and the chip. This is an undoubted advantage, as it is believed that the chip cannot be made at home, which, in turn, deprives the scammers of the possibility to make a fake card by releasing its duplicate with a copy of the magnetic strip track (so-called skimming). But often there is a situation where the seller of TSP, considering these card data from the magnetic strip (not from the chip), invites the client to confirm his consent with the commission of payment by introducing PIN. This is completely unacceptable, as the risk of full compromise the data of the card (i.e., the track / track of the magnetic strip and PIN), which theoretically can lead to the loss of all funds from the card account. Sellers explain their actions by the fact that the electronic terminal is already programmed, but most often the error is lighted in their actions: when working with this, they indicate that the type of card is not MasterCard, but Cirrus / Maestro. It is noteworthy that in the territory of the Russian Federation all operations on Cirrus / Maestro cards must be committed precisely as PBT!
Interesting fact: in the rules of the VISA MPS, it is indicated that in any case, when performing the operation of payment for goods or services in the TSP, the client has the right to demand the SBT operation. And it has a completely reasonable explanation: not all customers remember their pin and some banks generally produce cards without pin to them. Of course, all of the above refers to the cards with a magnetic strip. By chip cards, the overwhelming number of operations in TSP is confirmed by the client by entering the PIN.
Recently, MasterCard MPS has released a circular (operating bulletin), in which he has notified all the participants in the calculations that from June 8, 2012 on the territory of the Russian Federation, I am allowed to request IDUs to confirm with clients of operations on maps with a magnetic strip conducted in TSP.
Thus, at present, in the territory of the Russian Federation, when placing operations in TSP on cards with a magnetic strip of the MPS Visa, the PIN input is invalid, and the MasterCard is allowed on the cards with a magnetic strip. By cards with a microprocessor (t. N. Chip), PIN is practically required for both MPS.
Refusal to accept cards without the name of the holder
Many issuers to quickly enter the market use so-called non-interstalized, non-mean cards, on the front side of which there is only a number, a validity period, but there is no surname and the name of the client (also these data, respectively, are absent on the first track of the magnetic strip). The rules of the IPU are completely clearly designated that such maps are an absolutely legitimate means of calculations and should be taken on par with all other MPS products. Equarers in the instructions for sellers also specifically stipulate this moment, and nevertheless, quite often, unfortunately, it happens that sellers flatly refuse to accept such cards to pay. As arguments, sellers bring an argument that they have nothing to compare the name and name of the client (meaning the prohibited practice of the request for confirming documents mentioned above). Such actions of TSP employees also contradict world practice and are subject to elaboration from the banks of the accreets.
Increase price (surcharge) for the goods when paying by the map
As you know, when concluding an accuming contract with TSP, the Bank indicates the size of the so-called parcel compassion (commission), which will be charged (underpaid) with TSP for all operations on the map. This Commission varies on countries and types of TSP activities, taking into account the revolutions of the latter. For a reference point, it can be borne in mind the amount of about 1.5 - 2.5%. Thus, if the amount of the transaction is 1000 rubles, the bank-accurate will credit the amount for the settlement of this commission, that is, 975 - 985 rubles. The difference is the most important component of the activities of the Equilera and will be attributed to the account of operating income. This is a completely normal practical practice worldwide, and the opinion that it is unprofitable for TSP is no more than delusion: when paying in cash, other overhead costs arise, quite comparable to these "losses" for acquiring. This includes the expenses of the TSP on passing cash, their safe storage, collection, etc. and nevertheless, many TPSs practiced the establishment of allowances when paying for goods and services on cards, and the size of such "cheats" is approximately equal to the size of the Exarcharge Commission. This practice is completely unacceptable, which is uniquely stipulated in the rules of the MPS. In the same rules of the MPS, a peculiar loophole for TSP is given, namely: it is indicated that TSP is entitled to provide a discount for cash. That is, in general, the price of goods or services when paying on the card should not exceed the usual, but you can make a discount to the client if it pays in cash.
Refusal to accept an unsigned card
According to the rules of the MPS on the reverse side of the map, a special band must be placed, intended for a sample of signature of the legal card holder. When executing the payment operation of goods or services in the TSP, the cashier must offer to the buyer to confirm its readiness to pay the deal, or by entering PIN, or by signing the electronic terminal check. If the consent is confirmed by the signature, the cashier should blame the signature on the check with a signature sample on the circulation of the card. However, quite often, when receiving a map, the client does not affect its signature (which is a violation of the requirements of the MPS and carries an increased risk of illegal use of the card by frauds in case of its loss). Sellers of the TSP, seeing that the client offers them an unsigned card, often refuse to accept such a payment facility to pay, which is also unacceptable. According to the rules of the MPS, in such cases, the cashier should offer to the Buyer to present a document certifying the identity of the latter, containing a photo and sample signature, after which it is suggested to sign a map, to merge the signature with the sample in the document and then complete the transaction. If the buyer fails to present a passport and (or) to sign the card, the transaction should not be completed.
Setting the minimum purchase / goods price to pay map
Often there are situations when the store comes out a minimum amount, starting with which the seller agrees to accept the card to pay. For example, the purchase amount when paying the card should not be less than 100 rubles. (or 1000, 10 000, etc.). This practice is categorically unacceptable, since according to the rules of the MPS, the terms of payment of the card must fully comply with the terms of payment of cash.
Return procedure for goods and tools spent
It happens that for any reason the client wishes to return the purchased goods back. If the goods were paid by the card, then the money must be returned to the card account, and not in cash. Moreover, the return of funds should be carried out at the expense of the card that the initial payment was made. If the goods return back, the Employee of the TSP should arrange an appropriate operation on the electronic terminal (Refund / Credit - Return / Credit). As a result of this operation, the terminal is printed a credit check, which is a confirmation and reason for the return of funds to the payer's account. According to the MPS rules, the return of funds must be carried out within 30 days from the date of registration of the loan operation. In the absence of cash receipt to the card account after this period, the client may issue a claim in the issuer, and the funds will be returned to the complaint cycle with the basis of "credit not solumed".
Registration of checks on card operations
The MPS imposes very strict requirements for the contents of the checks of electronic terminals, printed on the basis of the completion of the operation. So, the following data should be specified on the check:
- description / Price of each paid product / service;
- date and time of operation;
- the amount and currency of the operation;
- map number (for security reasons Only the last four digits);
- country, city, address of the point or separation of the bank;
- the name of the TSP or DBA (Doing Business AS, DBA Name, for example, VimpelCom OJSC is known in the market as Beeline);
- authorization code (if was);
- type of operation (payment of goods, refund);
- place to sign up the client;
- place for the initials of the seller, cashier or other identifier (for example, the department number in the supermarket) unit serving the card;
- place to sign a seller (in the case of a loan operation);
- on the copy of the buyer, the text in Russian or English should be placed approximately the following content: "Important: Save this check to control operations in the discharge";
- other parameters in accordance with the requirements of local laws.
According to the requirements of the Bank of Russia on the checks of Russian TSP, it is necessary to place the text about the amount of the commission (usually they are written "Commission of the Board is missing"), charged from the buyer.
It is also necessary to have the text of approximately the following content: "This is the authorization of its bank-issuer to pay this purchase and binding to compensate the issuer the amount marked in the column" Total ", plus all the relevant commissions."
Customers must store copies of checks for at least six months to ensure the ability to control the correctness of the write-off of funds in their statements on operations with the card. The main purpose of the information on the check is to ensure the ability to definitely relate information reflected in the discharge with the data on the check. If the data on the check and in the discharge differ significantly, the client arises the right to issue a claim with all the resulting sad consequences for the parlor.
Consideration of claims on the facts of identified violations
In all cases, the description of which is given in this article to affordable buyers - bank card holders need to be applying to only their bank-issuer who has released a card. In this case, it will be necessary to submit to the bank such data as the exact address of the TSP, the name, date, time, identifier or the name of the Bank of the Equilera (if the operation on the card did not take place at all, i.e. authorization request was not formed and did not go to the network , the Issuer will not be able to determine these data on its own), and the essence of the claim (refusal to accept the card, the requirement to present a passport, introduce a PIN, etc.).
Obviously, it makes no sense to even try to contact the accreede bank, since in general the situation with violation of the rules for registration of operations with cards may occur anywhere in the planet and not always the victim will be able to find time for a visit to the right place and it is unlikely that he will Enjoy special knowledge and own terminology at the local adverium.
Based on such an appeal, the issuer has full right to send, in turn, a claim to the authorized body of the IPU, and a variety of sanctions can be applied to the Equarer - ranging from warning and requirements to conduct additional training of employees of the TSP-violators, up to the imposition of tangible financial fines (hundreds and Thousands of dollars or euros depending on the tariffs of the MPS).
Conclusion
In our dynamic age, when non-cash payments rapidly invade all areas of life, and operations with bank cards became everyday phenomenon, the aspect of client literacy is very important. This question includes both the basics of the proper use of cards in everyday situations and the nuances covered in this article, namely: what rights to have a buyer when paying for goods or services in a network of trade and service enterprises on the map and what exactly needs to be taken in case Detection of violations of procedures for issuing such operations.
Since international payment systems do not work with end customers (cardholders and TSPs), and with financial institutions and primarily care that their products (maps) are accepted everywhere and without restrictions, the acquirers are made very strict requirements in terms of warranty and compliance with MPS card reception procedures in the network of their TSP. In cases of identifying violations of procedures and conditions for receiving cards, holders should complain about issuing banks, which in turn have the right and obligation to inform the corresponding MPS on such incidents, which ultimately may result in highly unpleasant sanctions for the boards and incorrectly working TRSs and their employees.
September 2012
Escaring commercial and service enterprises through a payment intermediary (Serebryakov S.V.)
Placing the article: 09/11/2014
Almost every bank sooner or later begins to look for way out retail market. One of the most attractive products for individuals is the service of banking (payment) cards. However, in order to get the right to produce cards (emissions) and serve them in the network of their enterprises (acquiring), it is necessary at least to become a member of a particular payment system, mainly international.
At the beginning of the last decade, a very popular solution for the rapid exit of banks to the retailer was the so-called agency scheme, in which a sponsor bank, which is a full member of the International Payment System (hereinafter - the MPS), as a rule, larger, attracted smaller banks to Emissury and acquiring. And if in terms of emission questions from payment systems rarely arose, since maps of such submempics could be unambiguously identified (projects "Aegis", "New Age"), then with the acquiring from the MPS point of view, there were much worse: banks - agents, not being Members of payment systems, attracted trade and service enterprises (hereinafter referred to as TSPs), in which conditions favorable for fraud often arose.
Moreover, some TSP, concluding the accuming agreement with its bank, independently attracted other trading points, thus becoming a mini-bank or settlement center for the latter, as naturally, nor the MPS, nor the bank-accreter had before a certain pore representation.
Such activity led to the fact that about 10 years ago, the MPS categorically and for a long time banned the so-called agent schemes in the territory of the Russian Federation and only relatively recently gave a relaxation on this issue by introducing the concept of payment Facilitator (payable intermediary). This is a certain plus and new opportunities for the boards, but now, the science of bitter experience, the MPS rigidly regulated all aspects of both the registration of such intermediaries and work with them.
General requirements of international payment systems for payment intermediaries
The scheme of relations assumes that the Bank-Accuerer concludes an agreement with the payment mediator, and the one, in turn, is entitled to attract and enter into acquiring contracts with many TSPs, thus creating a peculiar tree structure (hierarchy). In this article, such TSPs will be called "subordinate TSPs".
In accordance with the rules and requirements of the MPS, the Bank-Equirer is fully responsible for any actions and errors of both subordinate TSP and the payment media itself. The payment intermediary, in turn, can no longer be a subordinate TSP of any other payment intermediary.
International payment systems impose tough restrictions on the total turnover: unless otherwise specified in the rules, any subordinate TSP, the total acquiring annual turnover of which on the MPS cards will exceed 100 thousand US dollars, must cease to be such and enter into direct contractual relations with the Bank Equirer.
The accreede bank must monitor compliance with the following requirements.
1. The payment intermediary and all its subordinate TSPs should operate only on the territory determined by the license to acquire their bank. The location of subordinate TSP is determined at the place of transaction, and not at the place of registration of the payment intermediary.
2. Means received by payment mediator should be used exclusively for payments in favor of subordinate TSPs.
3. The acquirer can allow the payment intermediary to implement the following activities on its own behalf, remaining fully responsible for the IPU for their adequate implementation:
- verification of subordinate TSPs on the correctness of doing business;
- Saving records about how a preliminary verification of subordinate TSPs was carried out, subject to the immediate presentation of such records at the request of the parlor;
- transfer to the accounts of subordinate TSS funds for transactions on the cards implemented in them;
- providing subordinate TSP by all materials necessary for successful transactions on maps;
- Monitoring the activity of subordinate TSPs in order to identify fraudulent activities or incorrect design of transactions.
Neither the payment intermediary nor his subordinate TSP is allowed to refuse the right to protest the operation.
The Equirer Bank is obliged to directly send a report on the work of each subordinate TST payment mediator in the IPU, which includes at least the following:
- the name of the subordinate TSP and its address;
- if applicable - link to the website of the subordinate TSP or the name of the brand;
- Merchant Category Code (MCC) - Table Description of Business Direction;
- for each MCC - the number and amount of operations on cards for the quarter;
- For each MCC - the number and volume of operations protested by issuers.
Payment Intermediaries and High-Neighted Commercial and Service Enterprises
International payment systems are assigned by the payment intermediary the status of high-roof, if he offers a sponsor bank subordinate TSP, whose business enters into a program of an increased number of protests (Excessive Chargeback Program) or corresponds to any of the MCC listed below:
- Telecommunications (MCC 4814, 4816);
- e-commerce video confant for adults (MCC 5967, 7273, 7841);
- Gambling via the Internet (7995), as well as payment for online games (7994);
- sales over Internet pharmacy goods and drugs (MCC 5122, 5912);
- Sales through Internet tobacco and similar goods (MCC 5993).
The Board should not register each of these TSPs in the relevant MPS program (for example, for MasterCard, this Merchant Registration Program (MRP)) before starting receiving transaction from them on cards.
Acting at its discretion, the MPS has the right to deprive the payment mediator when identifying an overpressure of protest operations or from the payment media itself, or from any of its subordinate TSPs or in violation of any of the requirements / standards of the MPS itself. The MPS also reserves the right to test the payment intermediary or its subordinate TSP in cases of identifying activities capable of harming the MPS.
Any acquirer who has entered into relations with a high-profile payment mediator must ensure the payment system of the monthly report on the activities of all subordinate TSPs in accordance with the rules of the MPS.
Registration requirements for payment intermediaries
In order to declare in the MPS on TSP as a payment intermediary, the acquirer should:
- be a member of the MPS with good status;
- meet all the requirements prescribed in the rules of the MPS;
- When registering a mediator who falls into the category of high-profile is to fully comply with all the rules and requirements of the MPS concerning risks and safety control issues.
For registration of TSP as a payment mediator, the fever should:
- send to the authorized division of the MPS all the necessary documentation and materials no later than within 60 days from the date of the proposed registration;
- Ensure the confidence that the mediator fully complies with such safety requirements as PCI DSS and other requirements applicable to situations.
Before sending financial information about the transactions of the payment intermediary or its subordinate TSPs to the MPS Settlement Network, the acquirer must receive written confirmation from the MPS (an email confirmation is allowed) on the successful registration of the payment intermediary. The decision to register a payment intermediary or a refusal to be taken by the IPU solely at its discretion.
To support the registration of the payment mediator, the Equirer is obliged to periodically send information to the IPU and documents that may be required to analyze, for example, a copy of the agreement between the equiar and the mediator. MPS reserves the exceptional right to refuse to extend the registration of the payment intermediary.
When making a payment intermediary, IPS will write all applicable to the parlor this process Commissions in accordance with current tariffs (for registration, consideration, updating license, etc.).
If the bank-acquirer intends to terminate the contract with an intermediary or subordinate TSP, it is necessary to notify the MPS on such a decision for no less than a week. MPS reserves the right to oblige the parlor immediately to stop taking operations from the payment intermediary at any time.
Responsibilities of the payment intermediary
The payment mediator is TSP and has all the rights and obligations applicable to the usual trading point.
The acquirer is charged with the obligation to ensure that the payment mediator meets all the requirements of the ICUs set out below.
Before entering into, to extend or update the agreement with the subordinate TSP, the payment mediator must make sure that this TSP is legitimate and correct business, has a sufficient set of mechanisms and procedures for reliable defense These cardholders and transaction holders from unauthorized access or disclosure, complies with all the necessary requirements and laws, and in addition, all transactions directed from such a TSP reflect the valid transaction between the subordinate TSP and the card holder.
The acquirer should make sure that the payment mediator is not a sponsor of the subordinate TSP registered in the database of unreliable outlets (for example, MATCH for MasterCard). Also, the acquirer is charged with the duty to send data to the relevant instances of the MPS on any subordinate TSP, contractual relations with which are discontinued due to the dubious activities of the latter.
Each payment mediator must conclude a written agreement with each subordinate TSP, where all conditions applied to the issue of receiving such TSP bank cards to pay. Such an agreement should not contradict or underestimate the rights of the payment intermediary, the Equilera or MPS in the matter of termination of its action at any time. MPS reserves prerogative to limit the payment mediator in the right to conclude agreements with the subordinate TSP, depending on the direction of business or other criteria at the discretion of the MPS.
Necessary points of agreement
Each agreement between the payment intermediary and the subordinate TSPs sponsored to them should reflect all the necessary conditions specified in the relevant sections of the MPS Rules, and other standards applicable to the essence of the TSP business, as well as to apply these standards in the same way as the usual TSP.
If the payment mediator does not register in the agreement with the subordinate TSP any necessary item provided for by the IPU Rules, or the special conditions specified by the MPS, this does not exempt the acquirer from responsibility on protest operations and other complaint procedures.
The agreement with subordinates of TSP should include the following provisions.
1. The subordinate TSP should continuously inform the payment intermediary about the current address of each of its offices, the names of the trade stamp used, along with complete description Sale goods and services provided.
2. If there is a contradiction between the rules of the IPU and any of the items of the Agreement between the payment intermediary and subordinate TSP, the provisions of the Rules are prevalent.
3. The payment mediator is fully responsible for compliance with the subordinate TSP standards and mapping procedures and has the right to demand from such a TSP to make changes to their website and other similar actions, if it seems necessary or reasonable to ensure that the Slave TSP compliance with the rules and standards of MPS .
4. The agreement with the Slave TSP is automatically and immediately considered invalid if the MPS degrees his payment mediator or the Bank-the Equarer ceases to be a member of the MPS for any reason, and also if the Equirer bank loses the MPS license to the acquiring.
5. The payment mediator at his discretion or instructions of the parlor / MPS has the right to immediately terminate the agreement with the subordinate TSP due to the activity that is fraudulent or doubtful from the point of view of the payment intermediary himself, the Equilera or MPS itself.
6. The subordinate TSP confirms and agrees that:
a) it complies with all applicable standards and rules of the MPS, which change from time to time;
b) MPS is the only and exclusive owner of their brands and signs;
c) subordinate TSP will never try to challenge the ownership of MPS trade brands for any reason;
d) MPS can at any time, immediately and without warning to prohibit the use of subordinate TSP of its trademarks for any purpose;
e) MPS has the right to strengthen any of the standards and prohibit subordinate TSP and (or) his payment intermediary participation in any activity, which from the MPS point of view may damage or create a risk of damage to the MPS reputation, and also clearly negatively affects the integrity of the MPS network or confidentiality of information;
(e) Subordinate TSP will never take any actions that may interfere or contradict the implementation of these RMS rights.
The agreement with the subordinate TSP should not contain any conditions that conflict with the current standards and rules of the MPS.
Responsibilities of the payment intermediary as a sponsor of a subordinate trade and service enterprise
The payment intermediary must strictly fulfill the following obligations towards each of its subordinate TSPs.
1. To send to the network only data on correct transactions.
The payment intermediary must transmit to its acquirer of the recording of correct transactions, transmitted by subordinate TSP and initiated by a genuine card holder. The payment mediator should not direct the Board of any transaction about which to which he or subordinate TSP probably should be known that it is fraudulent or not sanctioned by the cardholder, or probably / should be known that it is initiated by the cardholder in collusion with the subordinate TSP in Criminal purposes. It is assumed that subordinate TSPs are responsible for the actions of their employees, agents and representatives.
2. To ensure compliance of subordinate TSP standards of the MPS.
The payment mediator is responsible for ensuring that each of his subordinate TSPs meet the standards and rules of the MPS. The payment intermediary must take all the necessary and reasonable actions to ensure the continuous compliance of subordinate TSP standards of the MPS.
3. To maintain the relevance of information on subordinate TSPs.
The payment intermediary must continuously maintain up to date information about names, addresses and URLs (if applicable) of all its subordinate TSPs. The acquirer must ensure that the payment mediator sends such information on request in a timely manner on request.
4. Make payments subordinate TSP.
Each payment mediator should pay for its subordinate TSP for all transactions transferred to the Equilera on behalf of these TSPs. The agreement with subordinate TSPs may include an item that allows the payment intermediary to hold amounts on protested operations or other similar cases.
5. Ensure subordinate TSP materials.
Each payment mediator must regularly make sure that all his subordinate TSPs are provided with all the materials necessary for efficient work with cards and the direction of transactions to the MPS network in accordance with the standards and regulations for receiving cards.
6. Monitor subordinate TSPs.
Each payment mediator must continuously monitor the activities and use of MPS trademarks by all its subordinate TSPs for the purpose of early detection of fraudulent and incorrect activity and ensure continuous compliance with MPS standards. For compliance with this rule, minimum TSP monitoring standards are installed, which are applicable to all subordinate TSPs.
conclusions
The more democratic and flexible IPU approach to issues of building relationships between drug banks and their trade and service enterprises, in particular the legalization of the scheme using the payment intermediary (Payment), undoubtedly allows participants of the MPS to develop a network of faster pace, attracting all new and new TSP and creating entire hierarchical structures with more complex levels of subordination and relationships.
Nevertheless, the accuar banks should be extremely gently to choose the TSP as payment intermediaries and to comply with all the rules and requirements of the MPS, especially in terms of security issues and compliance with the standards for receiving maps to service in TSP.